H1: Beyond Chatbots: Giving Your n8n AI Agents “Hands” with Custom Tools
Welcome back to Day 25 of the 30 Days of n8n & Automation series here on whoisalfaz.me.
We have reached a pivotal moment in this series. We are moving from “Automation” to “Autonomous Agents.”
Let’s review the architecture we’ve built:
- Day 15: We built a basic AI Content Researcher.
- Day 22: We automated complex reporting PDF generation.
- Day 23: We secured our systems with a Global Error Watchtower.
- Day 24: We turned n8n into a serverless Backend API.
If you stopped right now, you would have an agency automation stack in the top 1%. But we aren’t stopping.
Today, we are going to connect the Brain (Day 15 AI) with the Backend (Day 24 API).
Standard LLMs (like ChatGPT) are “frozen in time.” They don’t know your client’s current subscription status. They don’t have access to your private database. If you ask a standard bot, “Is my account active?”, it will hallucinate an answer.
To fix this, we need n8n AI Agent Tools, often called Function Calling. We are going to give our AI a “backpack” of utilities—in this case, access to the API we built yesterday—so it can go fetch real-time data autonomously before answering the user.
The Concept: Why AI Needs “Hands” (Function Calling)
Before we build, you must understand the paradigm shift from “Prompt Engineering” to “Agentic Engineering.”
A standard ChatGPT prompt is passive:
User: “What is the capital of France?” AI: “Paris.”
An AI Agent with Tools is active. It reasons about the request and determines if it needs external help.
User: “Is the user ‘[email protected]’ active right now?” AI (Internal Monologue): “I do not know this information. I have a tool called ‘Verify User API’. I should use that tool with the email ‘[email protected]’.” AI (Action): Calls the API. receives
{"verified": true}. AI (Final Response): “Yes, Alfaz is currently active.”
In n8n, which uses LangChain under the hood, we define these “Tools” and give them to the AI Agent node. The AI then decides if and when to use them based on the conversation.
The Architecture: The “Tier 1 Support” Agent
We are going to build an autonomous support agent.
The Goal: A chatbot that can accurately answer questions about user account status without human intervention.
The Stack:
- The Trigger: A Chat Trigger ( simulating a website support widget).
- The Brain: The AI Agent node (using OpenAI GPT-4o or similar).
- The Tool: A Custom n8n Tool that connects to the Day 24 Verification API.
The critical part here is that we are not hardcoding the API call. We are teaching the AI how to make the call, and letting it decide when it’s necessary.
Step 1: The Brain (AI Agent Node Setup)
Start a new workflow.
- Add a Chat Trigger: This provides the chat interface for testing.
- Add the “AI Agent” Node: Connect it to the trigger.
- Configure the Model: Connect an OpenAI Chat Model node to the “Model” input of the Agent. Use a smart model like
gpt-4oorgpt-4-turbofor reliable function calling.
The System Prompt
This is where you define the agent’s persona. In the AI Agent node settings:
Text:
You are a helpful Tier 1 support agent for our SaaS platform. Your job is to assist users with account questions.
You have access to tools to look up real-time data. ALWAYS use the available tools to verify information before answering a user’s question about their account status. Do not guess. If the tool returns an error, report that error to the user.
This prompt is crucial. You are instructing it to rely on n8n AI Agent Tools rather than its training data.
Step 2: The Hands (Defining the Custom Tool)
This is the technical core of today’s tutorial. We need to define the “Tool Spec” so the AI understands what capabilities it has.
In n8n, look for the “Tools” category. Drag in a Custom n8n Tool node and connect it to the “Tools” input of the AI Agent node.
We need to configure three critical fields in the Custom Tool node:
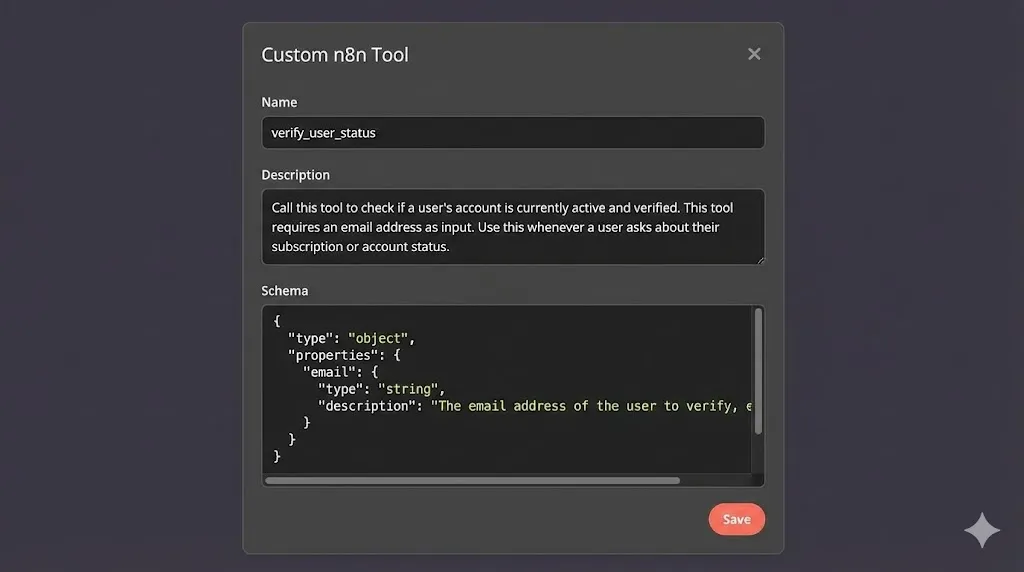
1. Name
Must be unique and descriptive.
- Value:
verify_user_status
2. Description (Crucial for AI)
This is NOT for humans. This is the instruction manual the AI reads to decide when to use this tool. It must be explicit.
- Value:
Call this tool to check if a user's account is currently active and verified. This tool requires an email address as input. Use this whenever a user asks about their subscription or account status.
3. Schema (Input Definition)
We need to tell the AI what data it needs to extract from the user’s prompt to use this tool. We need an email.
We define this using a JSON schema:
JSON
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"email": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The email address of the user to verify, e.g., [email protected]"
}
}
}
The AI now knows: “To use verify_user_status, I must find an email string.”
Step 3: Connecting the API (The HTTP Request)
Now that we have defined the abstract tool, we need to define the concrete action it takes.
The Custom n8n Tool is a sub-workflow wrapper. Double-click the Custom Tool node to open its internal canvas.
Inside, you will see a “Tool Workflow Trigger” and a “Tool Workflow Output.” We need to put the action in between.
- Add an HTTP Request Node: Place it between the trigger and output.
- Method: POST.
- URL: Paste the Production URL of the API you built on Day 24 (e.g.,
https://n8n.your-domain.com/webhook/verify-user). - Authentication: Use Header Auth and provide the API key you created yesterday.
- Body Parameters (JSON):
- Name:
email - Value: Drag in the
emailparameter from the “Tool Workflow Trigger” node on the left. (Expression:{{ $json.email }}).
- Name:
What just happened? We linked the AI’s concept of an “email input” directly to the JSON body of the API request.
H2: Step 4: The Execution (Watching it Think)
Let’s test our autonomous agent.
- Open the Chat window in the main workflow.
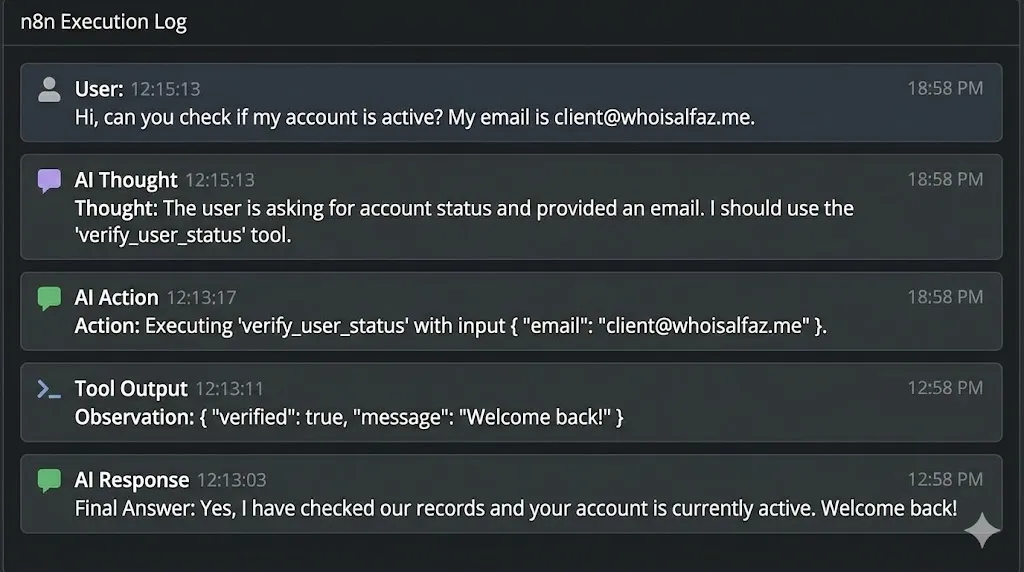
- Type: “Hi, can you check if my account is active? My email is [email protected].”
Watch the execution logs. This is the magic of Agentic AI.
You won’t just see a response. You will see a “Chain of Thought”:
- Thought: The user is asking for account status and provided an email. I should use the
verify_user_statustool. - Action: Executing
verify_user_statuswith inputemail: [email protected]. - (The internal HTTP request runs and returns
{"verified": true, "message": "Welcome back!"}). - Observation: The tool returned that the user is verified.
- Final Answer: Yes, I have checked our records and your account is currently active. Welcome back!
The AI didn’t just chat; it performed a secure backend lookup on its own initiative.
Real-World Agency Use Cases for AI Tools
Connecting ChatGPT to a simple API is just the beginning. By using n8n AI Agent Tools, you can build incredibly powerful systems:
- The “Database Query” Agent:
- Give the AI a tool that executes a read-only SQL query on your Postgres database.
- User: “How many leads did we get last week?” -> AI: Runs SQL query -> AI: “You received 145 leads.”
- The “Booking Assistant” Agent:
- Give the AI access to the Google Calendar node as a tool.
- User: “Book a meeting with Alfaz for tomorrow at 2 PM.” -> AI: Checks availability, creates the event.
- The “Troubleshooter” Agent:
- Give the AI access to your server logs via an API.
- User: “Why is my site down?” -> AI: Check recent error logs -> AI: “It looks like a database connection timeout occurred 5 minutes ago.”
Conclusion: The Era of Autonomous Automation
By combining the cognitive power of LLMs with the connectivity of n8n AI Agent Tools, we have moved beyond simple automation scripts. We are now building systems that can reason, plan, and act autonomously.
This is the future of agency automation. It’s not just about moving data from A to B; it’s about having intelligent agents manage the process for you.
What’s Next? We have built agents that can use tools. But what if the data they need isn’t in an API, but buried in a 100-page PDF contract? Tomorrow, on Day 26, we dive into RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation). I will show you how to build a “Knowledge Base” that your AI agent can read before answering questions.
See you in the workflow editor.
External Resources:
- n8n AI Agent Node Documentation
- OpenAI Function Calling Guide (The underlying technology used here).
- LangChain Concepts (The framework n8n uses for agents).
